
This first post in this series focuses on the obvious first question to address: are we dealing with a Louisiana sales tax issue or a Louisiana use tax issue (or perhaps both)? Which tax is applicable, and which Louisiana statutory tax provisions are to be utilized?
The interplay of sales tax and use tax in

 Monday’s meeting in Baton Rouge of the
Monday’s meeting in Baton Rouge of the  As word spread about the Supreme Court’s opinion in
As word spread about the Supreme Court’s opinion in 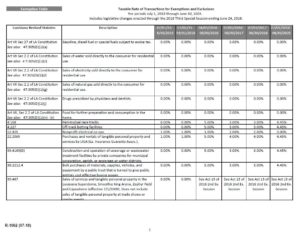 The Louisiana Department of Revenue has now issued a revised
The Louisiana Department of Revenue has now issued a revised 